CI/CD - Integrate With GitLab CI Pipelines
Introduction
This article helps you to quickly configure your project for integration with GitLab CI Pipelines.
Every templates comes with the .gitlab-ci.yml file configured to build and create the application package on the Torizon Cloud.
Pre-requisites
- GitLab account
- GitLab Repository
- Torizon Cloud API v2 Client
- Torizon Cloud credentials.zip
- Project
fill-pipeline-settingstask executed at least once. See the respective Workspace Task for more information.
Configure the GitLab Repository
After creating the GitLab repository, you need to configure the secrets and variables to be used in the GitLab CI pipeline.
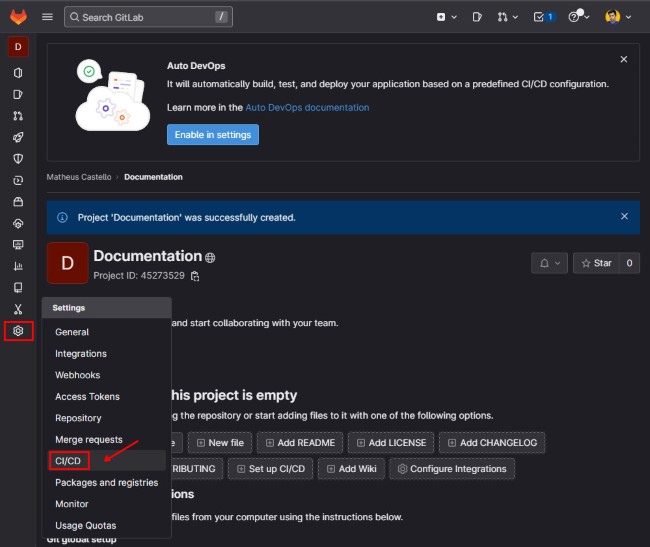
- In the repo page, mouse hover in the
Settingsand click on theCI/CD:
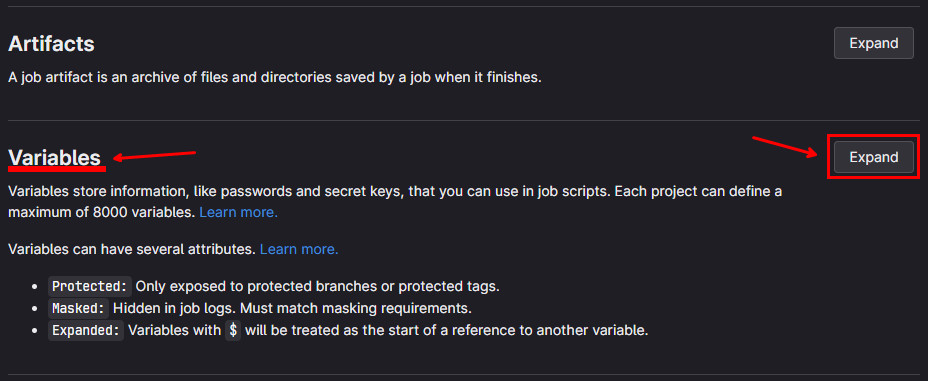
- Click on the
Expandbutton fromVariablessection:
- Click on the
Add variablebutton:
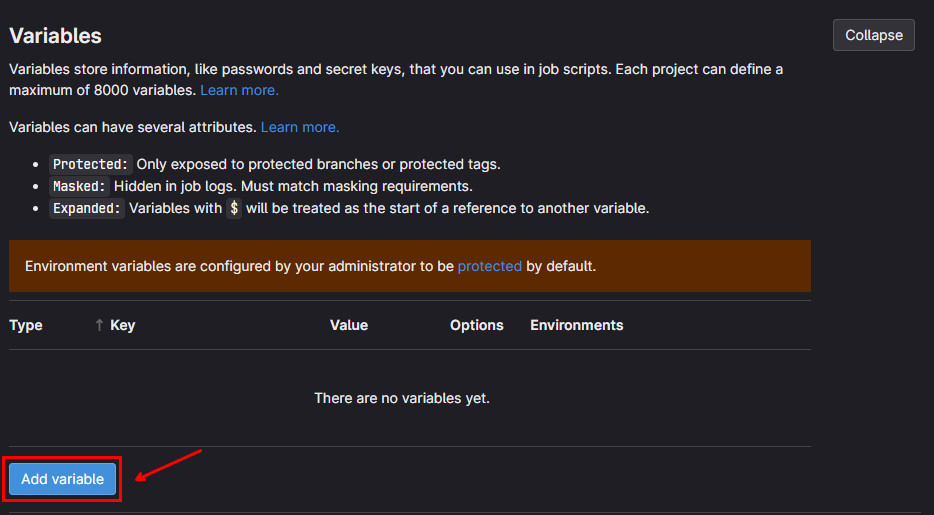
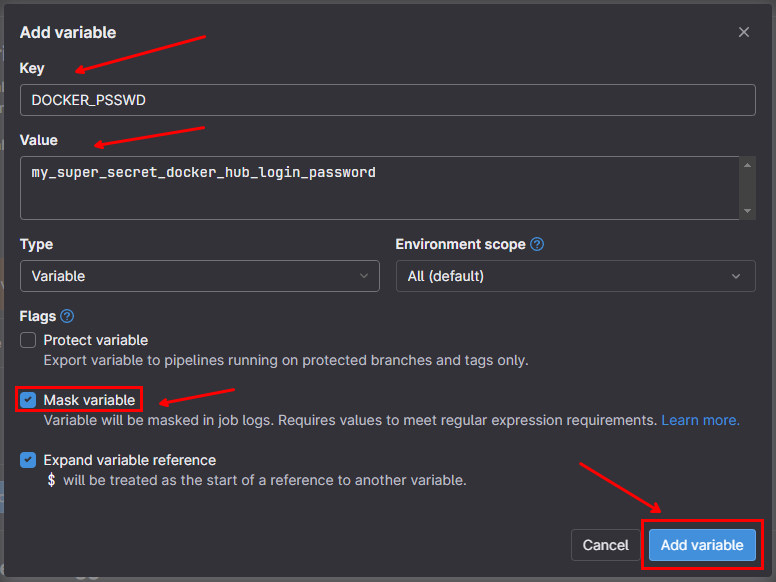
This will open the Add variable modal window. In the Key field, type the name of the variable. In the Value field, type the value of the variable. Also make sure to check the Mask variable checkbox for the secret data. Then, click on the Add variable button:
In GitLab CI is possible also protect variables to be used only in the protected branches, see GitLab CI/CD variables for more information.
Then, you will see the variable added to the list:
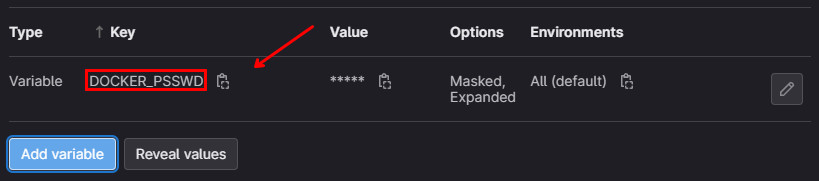
Do it for all the secrets listed below:
DOCKER_PSSWD: DockerHub registry login password. This is the password from the login name that comes from thedocker_loginproperty, from.vscode/settings.json, see Workspace Settings for more information.PLATFORM_CLIENT_ID: Torizon Cloud API v2 Client ID. See Creating a New Torizon Cloud API v2 Client for more information.PLATFORM_CLIENT_SECRET: Torizon Cloud API v2 Client Secret. See Creating a New Torizon Cloud API v2 Client for more information.
Adding credentials.zip as CI/CD Variable
To use the TorizonCore Builder to create the Torizon Cloud package, we need the credentials.zip file available in the CI/CD pipeline. The .gitlab-ci.yml expectes to have the PLATFORM_CREDENTIALS variable with the base64 encode of the credentials.zip file. Execute the follow command to get the base64 encode of the credentials.zip file:
base64 -w 0 ./credentials.zip
Then, add the PLATFORM_CREDENTIALS variable, with the output from command as value.
Make sure to check the Mask variable checkbox for PLATFORM_CREDENTIALS variable.
Running the CI/CD Pipeline
After configuring the variables needed, your GitLab repository is ready to run the GitLab CI pipeline. Simply push your changes to the repository and the pipeline will be triggered automatically.
The following jobs will be executed:
Initial Setup: This step will verify the environment variables and secrets configured in the repository. If any of the required variables are missing, the workflow will fail fast in this first step;build-docker-image: This step will run the taskcreate-production-imagetask. This task will create the production image and publish it to the Docker registry. See the respective Workspace Task for more information.push-package-to-platform: This step will run the tasktcb-platform-publish. This task will create the Torizon Cloud package and publish it to the Torizon Cloud. See the respective Workspace Task for more information.update-fleet: This step will run the taskplatform-update-fleet. This task will update the fleet with the new package. See the respective Workspace Task for more information.
The update-fleet job will only be executed for a push on the main branch. If you want to trigger an update when pushing in a different branch, you need to change the if condition in the update-fleet step from the .gitlab-ci.yml file. Check the templates repository file: https://github.com/toradex/vscode-torizon-templates/blob/bookworm/assets/gitlab/.gitlab-ci.yml#L101
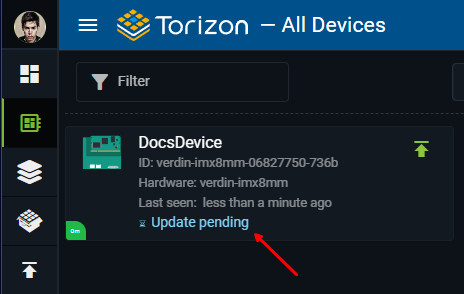
At the end of the pipeline, if all occurs as expected, you will have the following in the pipeline page:
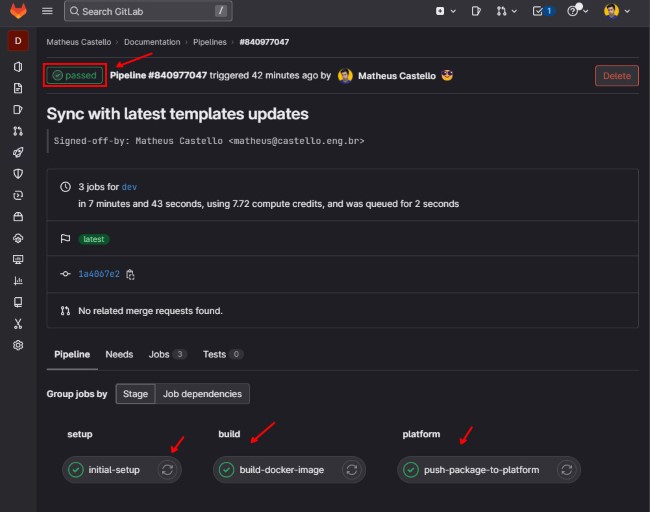
And the Torizon Cloud update will be triggered, you should have the devices from the fleet with Update pending state: